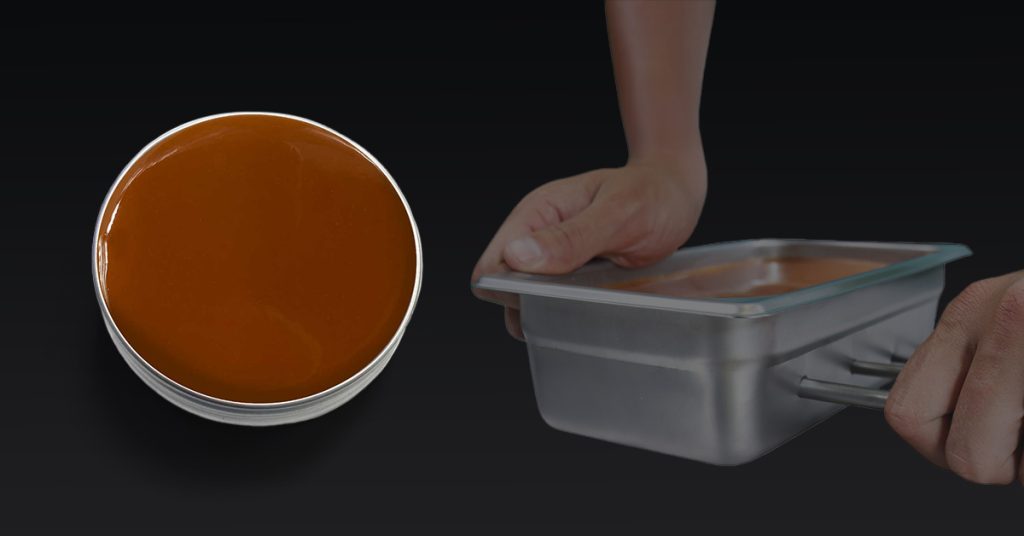


Brown dye might seem like a basic colorant, but how it’s made—and where it’s used—tells a more interesting story. In fact, brown dyes show up in everything from clothing and makeup to tools used in medical training.
At Humimic Medical, we use a special brown tone dye to help make our clinical models look more like real human tissue. When training tools look realistic, they help people learn better and feel more confident when it’s time to apply those skills in real life.
In this article, we’ll look at the different types of brown dyes, how they’re made, and why choosing the right kind of brown matters in medical simulation.
Brown dye is created using either natural or synthetic sources, each offering different benefits depending on the material, purpose, and environment. Understanding these sources helps manufacturers, educators, and developers choose the right formula for the job, especially in technical fields like healthcare simulation.
The two main categories of brown dye sources—natural and synthetic—each offer distinct advantages depending on the use case.
Natural brown dyes are derived from plants and organic matter. These are commonly used in textiles, artisan crafts, and traditional cosmetics. Examples include:
While these sources are biodegradable and generally safe, they can be inconsistent in color strength and performance, making them less ideal for high-precision training tools.
Synthetic dyes are engineered for consistency, longevity, and controlled pigmentation. They’re widely used in manufacturing, medical models, cosmetics, and plastics. Common synthetic sources include:
Synthetic options provide more predictable results, making them suitable for environments that demand visual accuracy and repeatable use.
In medical simulation, realistic color isn’t just aesthetic; it supports effective learning. That’s why Humimic Medical formulates a proprietary brown tone dye to pair with our synthetic tissue systems. While we don’t disclose the full formulation, our focus is clear:
Our brown tone dye is purpose-built to help educators and clinicians create simulation models that feel closer to reality. Training becomes more effective when the visuals reflect what learners will encounter in real life.
Brown dyes are grouped based on how they are sourced, what they are made of, and how they behave when applied. These brown dyes differ in performance and application, especially in clinical or simulation settings. For simulation and training tools, selecting the right type of dye can make a visible difference in performance.
This category explains whether it comes from organic materials or is developed through chemical processes.
This classification refers to the chemical structure of the dye and how it interacts with surfaces.
This type is based on the liquid carrier used in the dye and how it applies to materials.
This is a highly adaptable pigment that is used in everyday products and specialized tools. It appears in what people wear, apply, manufacture, and even use for clinical training. Each application calls for a different formulation and level of precision.
Brown dyes are widely used to color natural and synthetic fabrics. It brings warmth and neutrality to garments such as uniforms, outerwear, and naturally dyed fashion. Designers often choose brown for its earthy tones and broad appeal.
The cosmetic industry relies on this pigment to deliver realistic, wearable shades in makeup and hair treatments. It is found in brow pencils, contour palettes, foundations, and various hair dye formulas. In this space, color reliability and skin compatibility are essential.
Brown dyes are commonly used to treat leather items like belts, shoes, wallets, and bags. These are often oil-based to provide a lasting finish. This type of pigment is also applied to plastics for tools, hardware parts, and molded surfaces that benefit from a more natural appearance.
At Humimic Medical, brown dye is part of how we help people train to save lives. Our specialized brown tone dye is used to color synthetic tissue, skin layers, and anatomical components in simulation models.
In medical training, accurate color matters. It helps learners identify anatomical landmarks, see variations across different layers, and engage more fully with the task. The more realistic the model looks, the better it supports skill-building and decision-making.
Simulation tools should reflect real human features, not just in form but in tone. That is why thoughtful pigmentation makes a difference in how training translates to real-world care.
Our brown tone dye isn’t repurposed from textiles or cosmetics. Realistic color and material compatibility make the training experience more effective and easier to translate into real-world care. Here’s why simulation professionals choose it:
This dye is ready to use and made for seamless application in simulation and testing environments. To get the best results, follow these basic guidelines:
✓ Application – Shake well before use. Apply directly to synthetic materials in controlled amounts. A little goes a long way.
✓ Handling – The formula is non-toxic, but we recommend using gloves to avoid staining. Clean any spills with mild soap and water.
✓ Storage – Keep the bottle sealed and stored in a dry, room-temperature location. When stored properly, the dye maintains its quality over time.
These tips help ensure color accuracy and product longevity across multiple training sessions.
Brown dye is more than a finishing touch. From traditional uses in textiles and cosmetics to high-precision simulation tools, its role continues to evolve. In medical training, the right shade can support a more realistic experience; one that helps learners connect what they see with what they do.
Humimic Medical’s brown tone dye is made for this purpose. It supports educators, lab managers, and R&D teams who rely on consistent color, safe handling, and true-to-life results.
If your work depends on visual realism, consider how a small detail like pigmentation can make a lasting difference in training outcomes.
Add to cart now and make your training simulation mimic real-life emergencies.
It’s optimized for synthetic tissue and anatomical models. For textiles or leather, other dyes may be more suitable.
Humimic Medical’s dye is formulated for long-lasting pigmentation on synthetic surfaces under typical usage conditions.
Yes, it’s designed for easy application and cleanup in simulation environments.
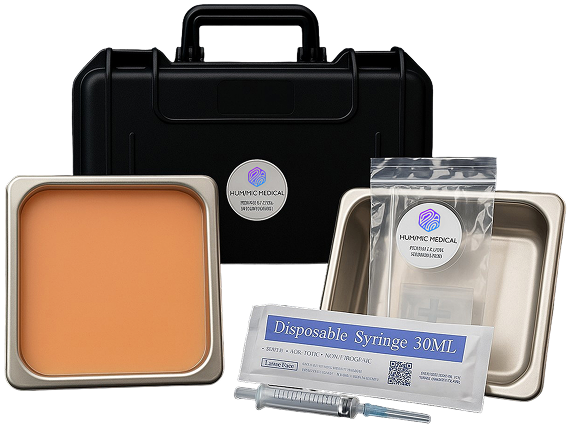



We design trauma trainers, gel models, and procedural tools customized to your exact use case — all powered by Humimic SimuGel™.